Drug distribution in pharmacology
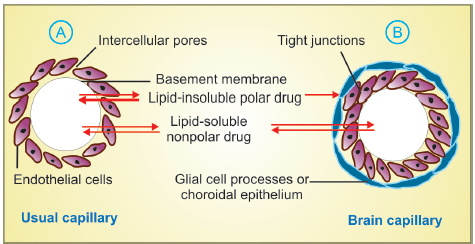
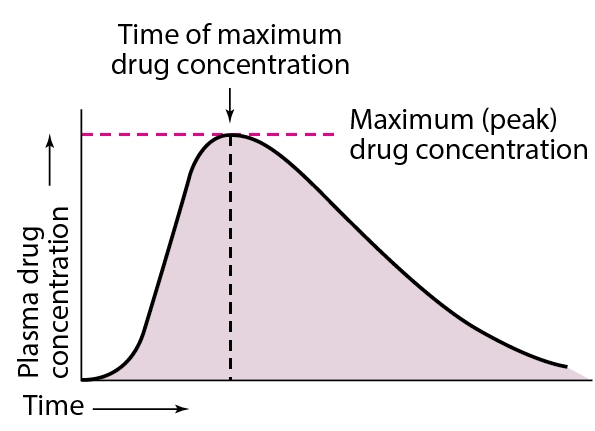
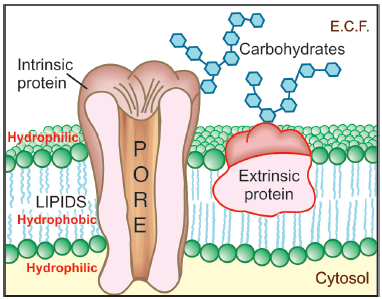
Drug distribution Drug distribution: Once a drug has gained access to the bloodstream, it gets distributed to other tissues that initially had no drug, concentration gradient being in the direction of plasma to tissues. The extent and pattern of a drug’s distribution are determined by its: lipid solubility ionization at physiological pH (a function of … Read more