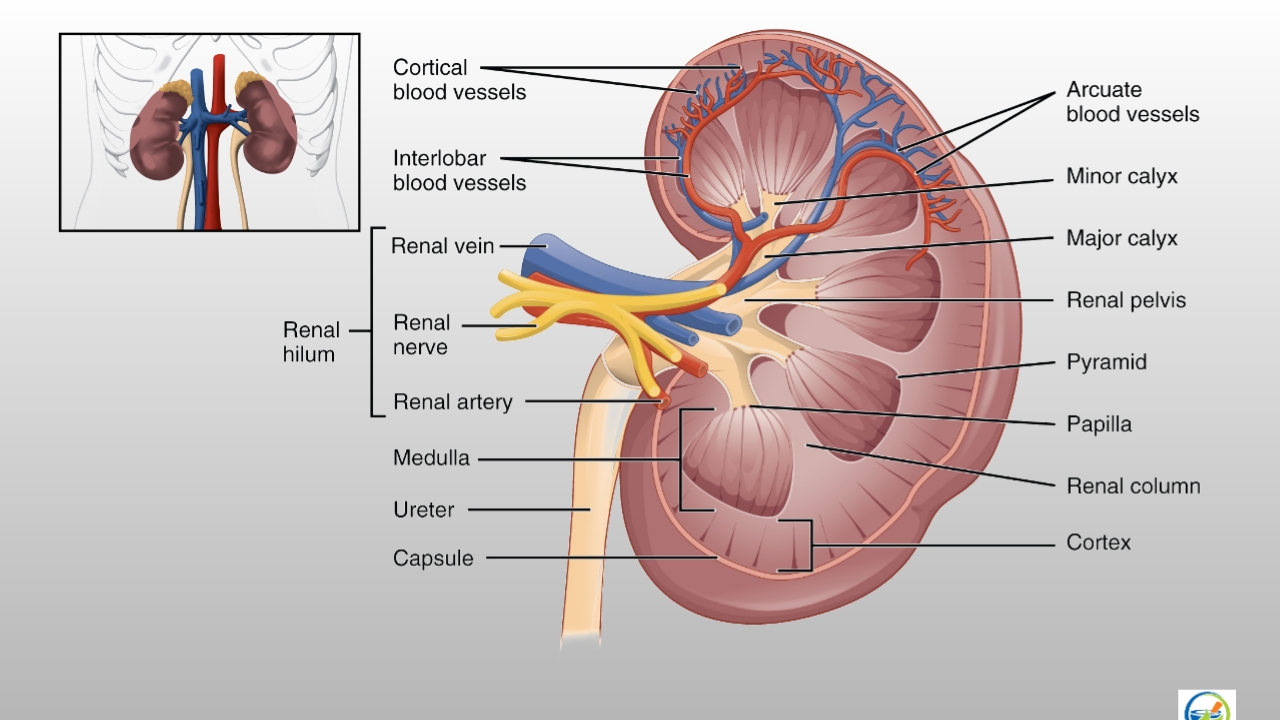
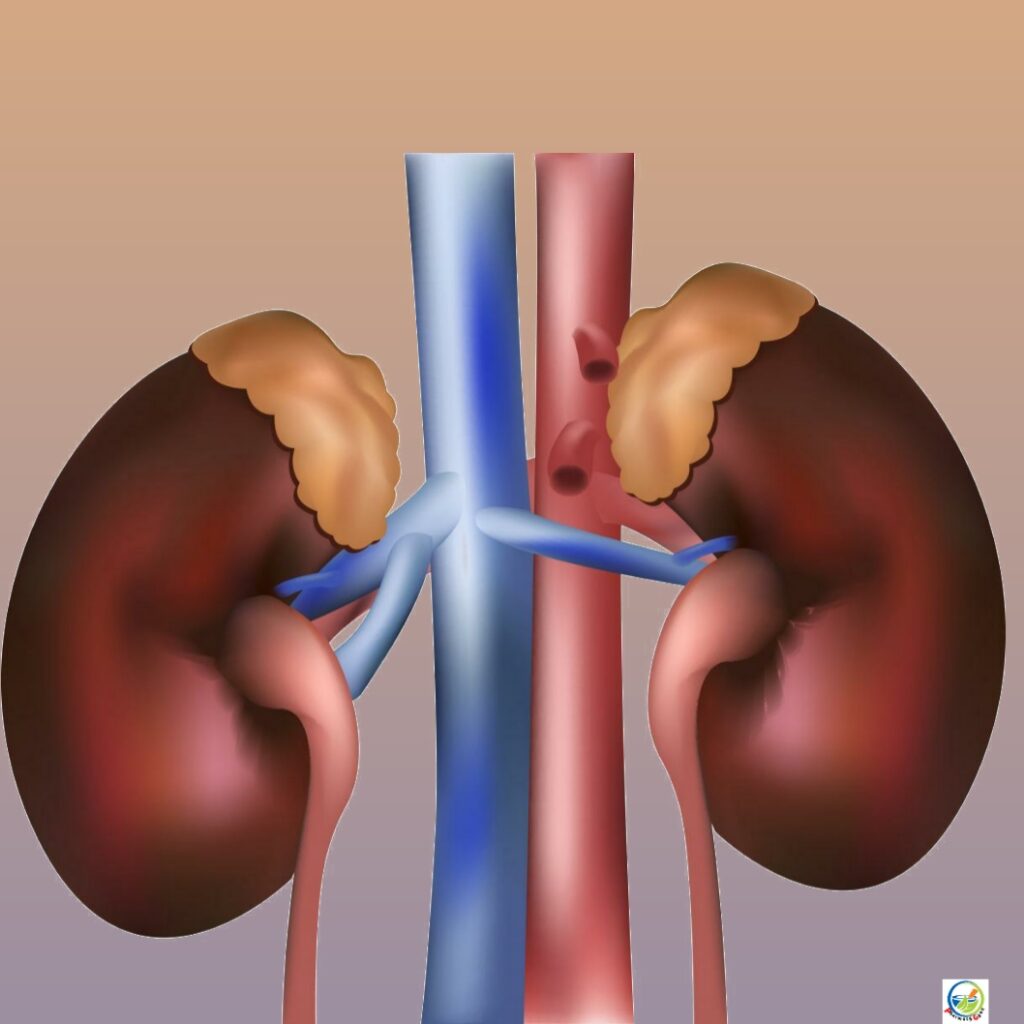
Anatomy of kidney: The kidneys lie on the posterior abdominal wall, one on each side of the vertebral column, behind the peritoneum and below the diaphragm. The right kidney is usually lower than the left because of the considerable space occupied by the liver.
Kidneys are bean shaped organ about 11 cm long, 6 cm wide, 3 cm thick and weight around 150gms.
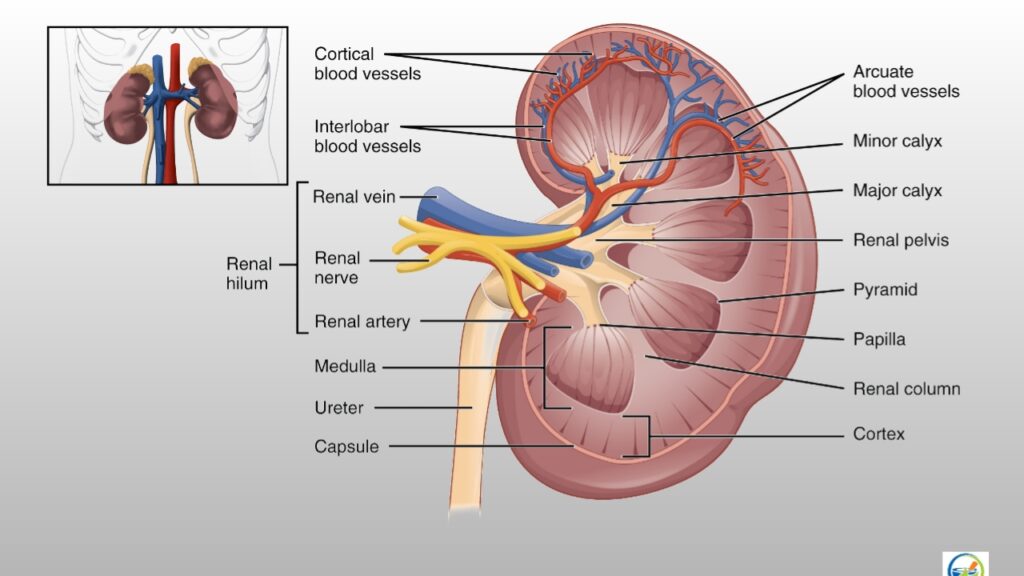
- Kidney consists of a fibrous capsule surrounding the kidney, the cortex a reddish brown layer of the tissue, and on inner side there are projections called pyramids and hollws called calyces
- Minor and major calyces unite to form dilated part called pelvis of the kidney.
- The pelvis terminated into tubular structure called ureter, which opens into the urinary bladder.
- The urine formed in the kidney is transported to the urinary bladder through ureters. Urinary bladder passes the urine out through a tube called urethra .
- In males the urethra is common passage for urine and semen, in females the urethra opens independently to the exterior.
The main functions of kidney are as follows:
- Formation and secretion of urine.
- It maintains water equilibrium, pH equilibrium, osmotic equilibrium and ionic equilibrium of the blood
- Production and secretion of erythropoietin hormon that controls formation of red blood cells.
- It excretes the waste products in dissolved form. There are the nitrogenous and sulphur containing end products of protein metabolism.
- Production and secretion of renin an important enzyme in the control of BP.
- It excretes poisonous and foreign substances from body. This includes drugs, toxins etc.
- It synthesis new substances namely ammonia, hippuric acid and inorganic phosphates.