Respiratory system is the system through which every cells in the body receive it oxygen and excretes its carbon dioxide. Lungs inhale and exhale the air through respiratory passages. The process of respiration may be divided into two types.

- External respiration
- Internal respiration
Function of respiration:
- Exchange of gases: They carry oxygen from lungs to the tissues and bring back carbon dioxide from tissues to the lungs for expiration through lungs.
- Maintenance of pH: This is carried out by balancing excretion of carbon dioxide.
- Excretion: Volatile substances like general anaesthetics like ether, ketone, bodies, ammonia are excreted through lungs.
- Metabolic function: It helps in maintaining the homeostasis of metabolism in the tissue.
- Temperature regulation: Heat is lost through the expiration air.
- Water regulation: Water vapour is excreted during respiration from the lungs.
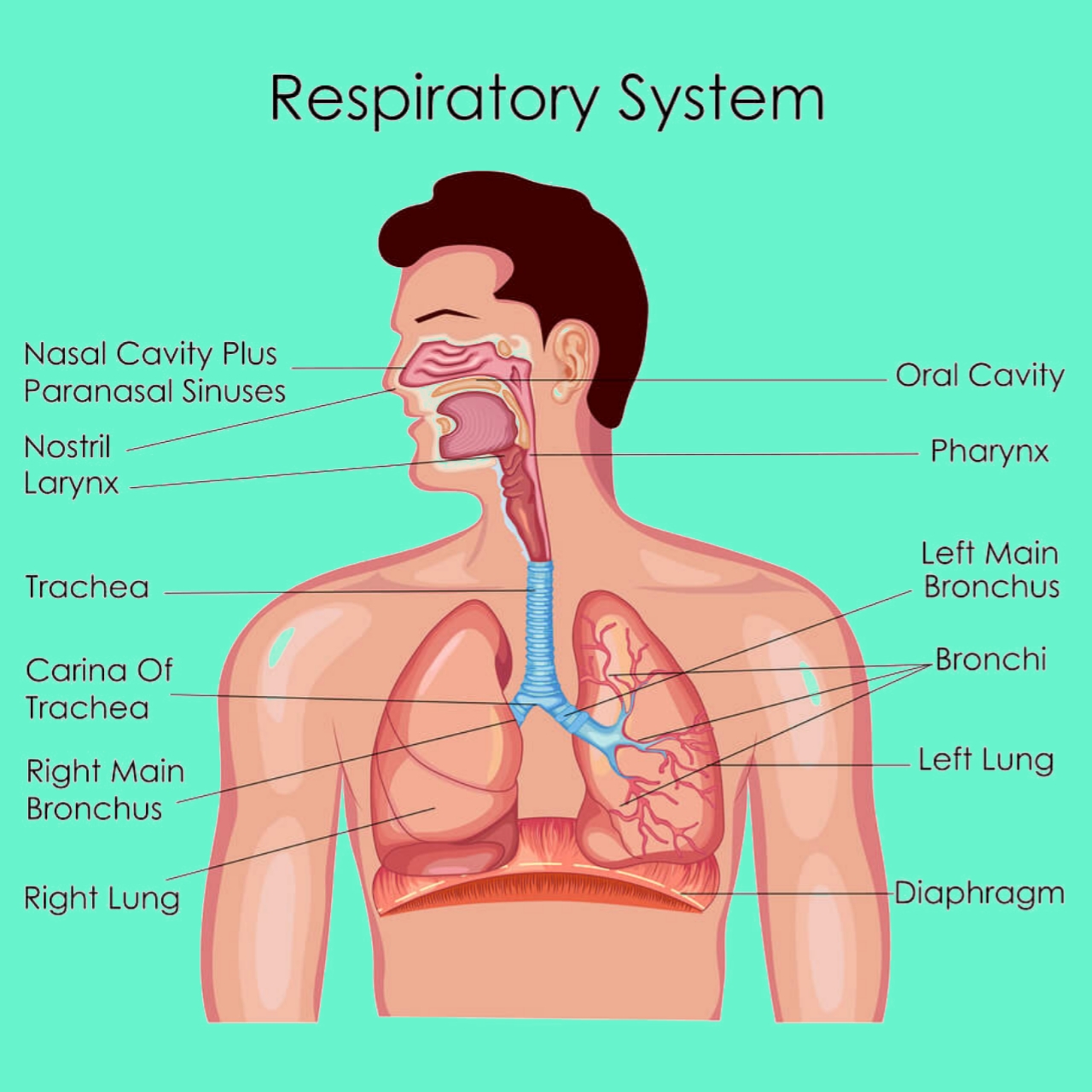
Anatomy of the respiratory system:
The organs of the respiratory systems are:
- Nose and nasal cavity.
- Pharynx.
- Larynx.
- Trachea.
- Two bronchi (one bronchus to each lungs)
- Two lungs.
- Muscle pf breathing- intercostal muscles and diaphragm.