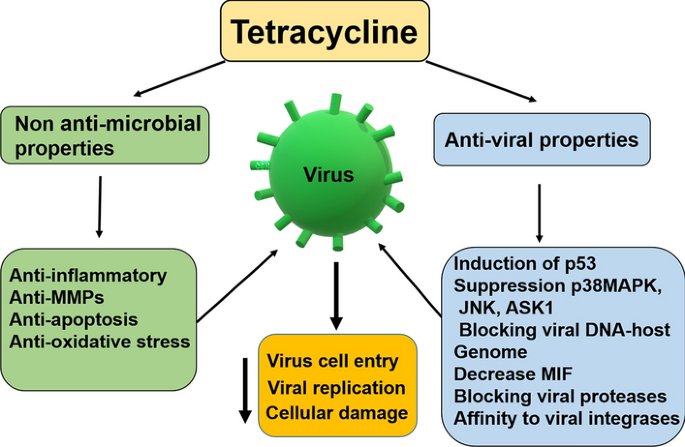
What is Tetracyclines?
Tetracyclines are the octahydro napthacene ring ( four membered ring) this are bacteriostatic and broad spectrum antibiotic that kill the certain infection causing bacteria or microorganism and its used to treat variety of infection.
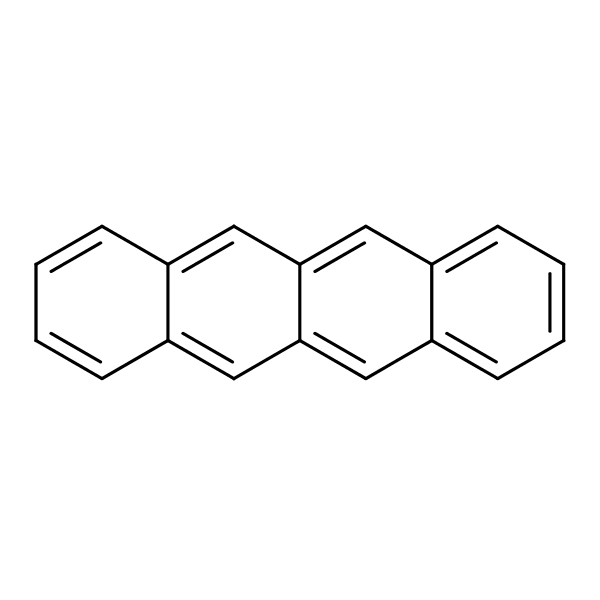
Tetracyclines are a large family of antibiotics are discovered in the form of chlortetracycline and oxytetracycline as natural product.
HISTORY OF TETRACYCLINES(TCS)
- In 1940s a 71 years old benjamin minge identified tetracyclines from soil micro-organism.
- At early stages tetracyclines was produced by fermentation of bacterium called streptomtyces aureofacians.
MECHANISM OF ACTION
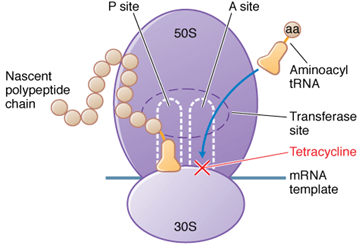
- This type of antibiotic are specific inhibitor of bacterial protein synthesis.
- They bind to the 30s ribosomal subunit and prevent the binding of aminoacyl tRNA-ribosome complex, which initiate the protein synthesis.
- There are two type of binding site (A-site and p-site) for tRNA molecule, p-site or peptidyl binds the tRNA bearing the peptide chain, The A-site or Acceptor aminoacyl site.
- Tetracyclines are reversibly binds to the 30s subunit at the A-site to avoiding attachment of the amino acyl tRNA, termination the translation process.
Bacterial ribosomes are 70s particles made up of 30s and 50s subunits. The 30s subunits are binds with the mRNA and inaugurate or initiated the protein synthesis and 50s subunit are combines with the 30s subunit mRNA complex to form a ribosome then binds aminoacyl tRNA and catalyses the making of protein chain.
STRUCTURE -ACTIVITY RELATIONSHIP(SAR):
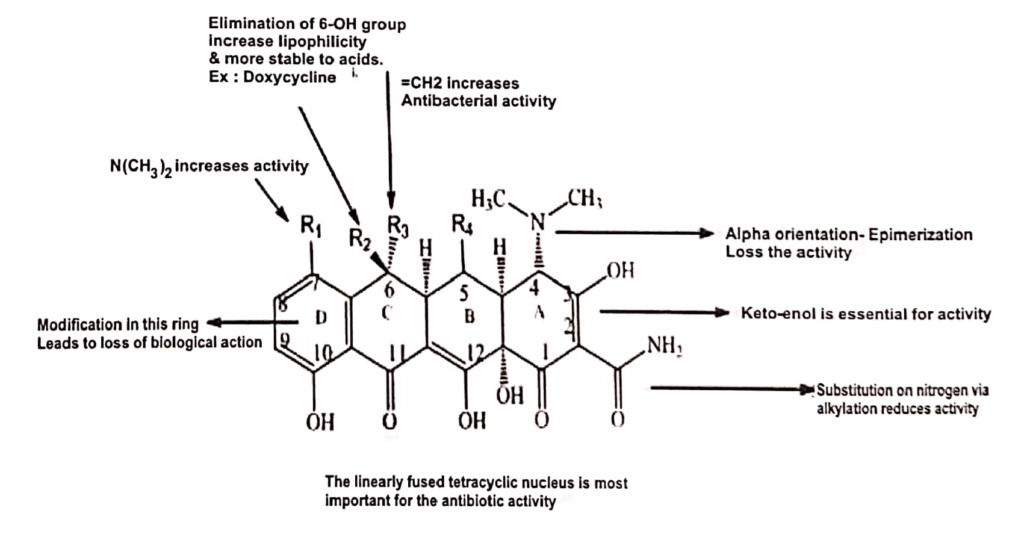
- On nitrogen substitution of alkylation reduces the activity.
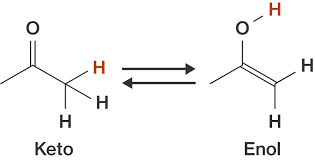
- Keto-enol on C2 AND C3 is essential for activity.
- The dimethylamino group at 4-position must have the alfa-orientation: removal of the 4- dimethylamino group reduces the activity.
- Substitution with -OH or hydroxyl at C-5, produced water soluble derivatives which can be administered orally only. ex: methacycline
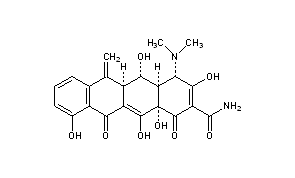
- =CH2 substitution at R3 increases the antibacterial action of drug molecule.
- Alkylation at C-11a leads to loss of activity of drug molecule.
- Substitution of electron withdrawing group(eg: chloro and nitro) and electron -donating group(dimethylamino) at C-7 increase the activity.
- D-ring must be aromatic, changes of D ring system leads to loose the biological action.
- Substitution of -OH group at the position C-5 and C-6 decrease lipid versus water solubility of the tetracyclines.
- Substitution of OH at C-6 increases lipophilicity and more stable to acids.
OFFICIAL DRUGS
TETRACYCLINES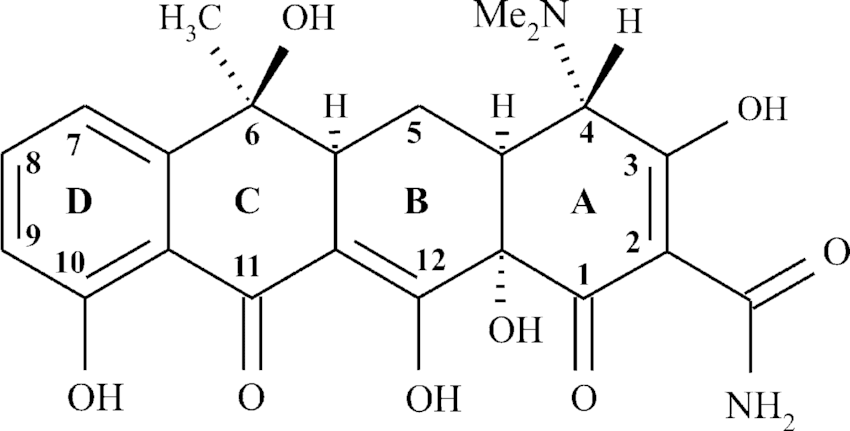
Uses: Treatment for Gonorrhoea, respiratory tract, ear infection and acne vulgaris.
CHLORTETRACYCLINES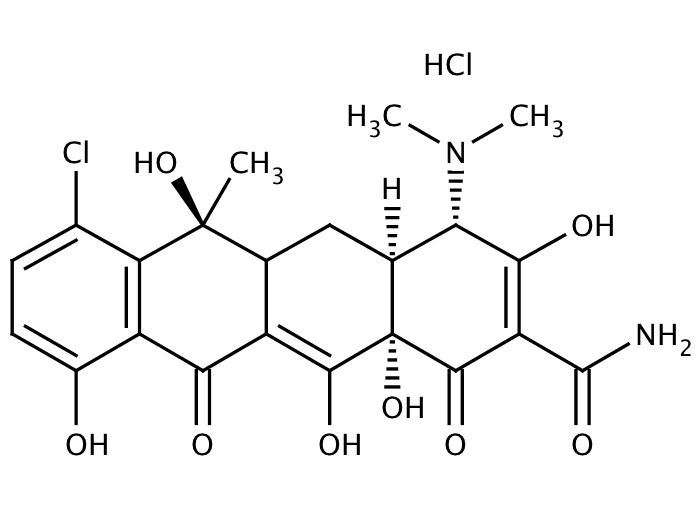
Uses: It is used to treatment for respiratory tract infection, middle ear infection, intestine and eye infection and skin infection.
DOXYCYCLINES 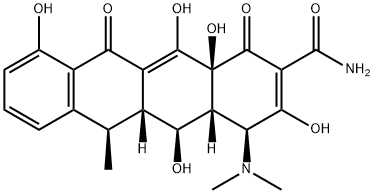
Uses: Used to treat respiratory tract infection and eye infection, urinary tract infection
Recently its used in prevention of cancer recurrence.
MINOCYCLINE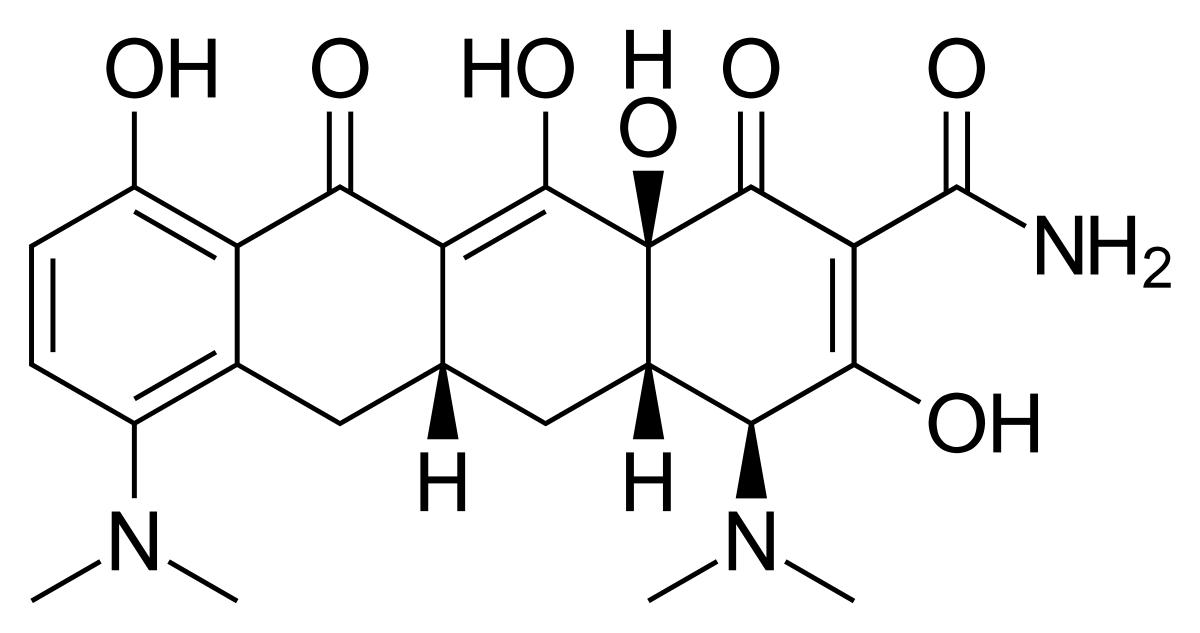
Uses: Used to treat respiratory tract infection and eye infection, urinary tract infection.
It is useful in the leprosy infection..
It is used in treatment of syphilis, sinusitis, oral herpes simplex and acne.
OXYTETRACYCLINES 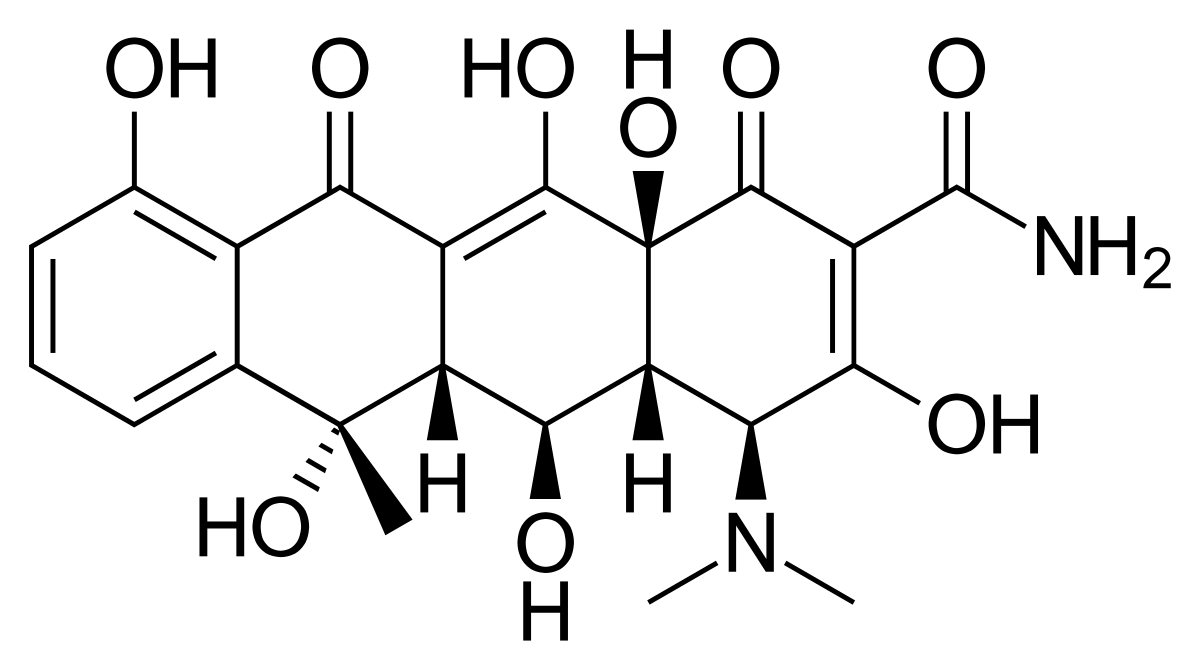
Uses: It is used to treatment of infections caused by gram+ve and Gram-ve bacteria, like the respiratory tract, eye infections and urinary tract infections.