It include Alimentary tract and Accessory organs.
Alimentary tract ; its also known as gastrointestinal tract and is a long tube thought which the food passes , it starts from the mouth and ends at anus, the various parts are:
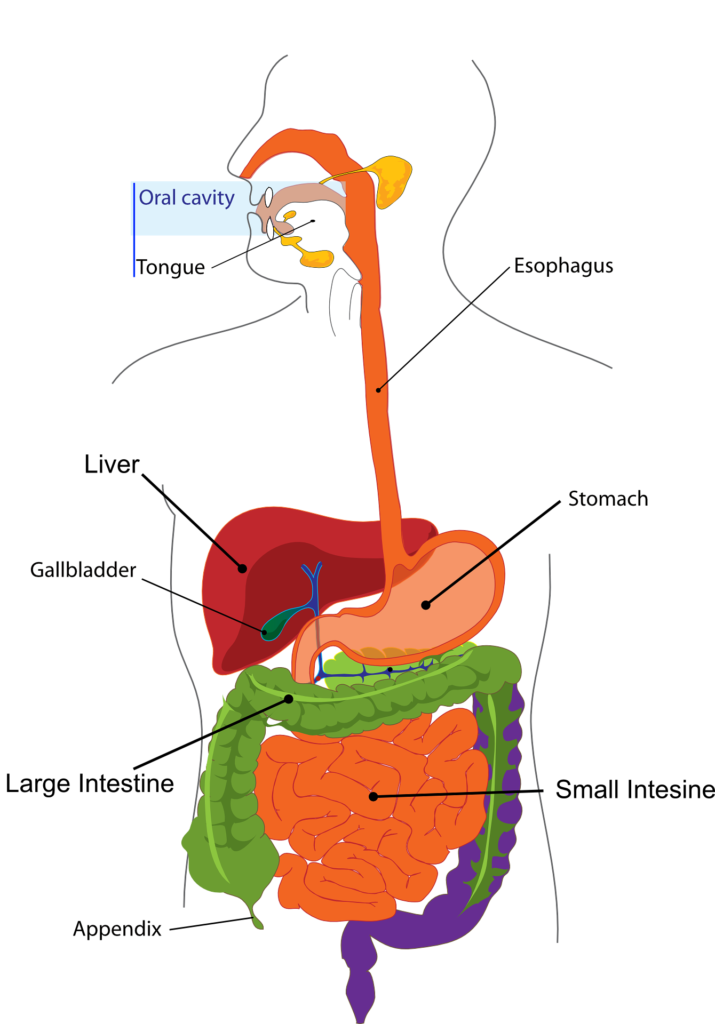
- Mouth / oral cavity
- Pharynx
- Oesophagus
- Small intestine
- large intestine
- Rectum and Anal canal
The accesory organs include:
- 3 pairs of salivary glands
- Pancreas
- liver and biliary tract
Mouth/oral cavity: The oral cavity is lines with the mucus membrane consisting of stratified squamous epithelium containing mucus secreting glands. The palate forms and roof of the mouth and is divided into anterior hard palate and posterior soft palate and pharyngeal tonsils are present on either side which protect against the infections. In the oral cavity fod is teared and grinded with the of teeth and is mixed thoroughly with the saliva. The process of tearing, grinding and mixing with saliva involves movement of jews, cheeks, lips and tongue. The process is known as mastication.
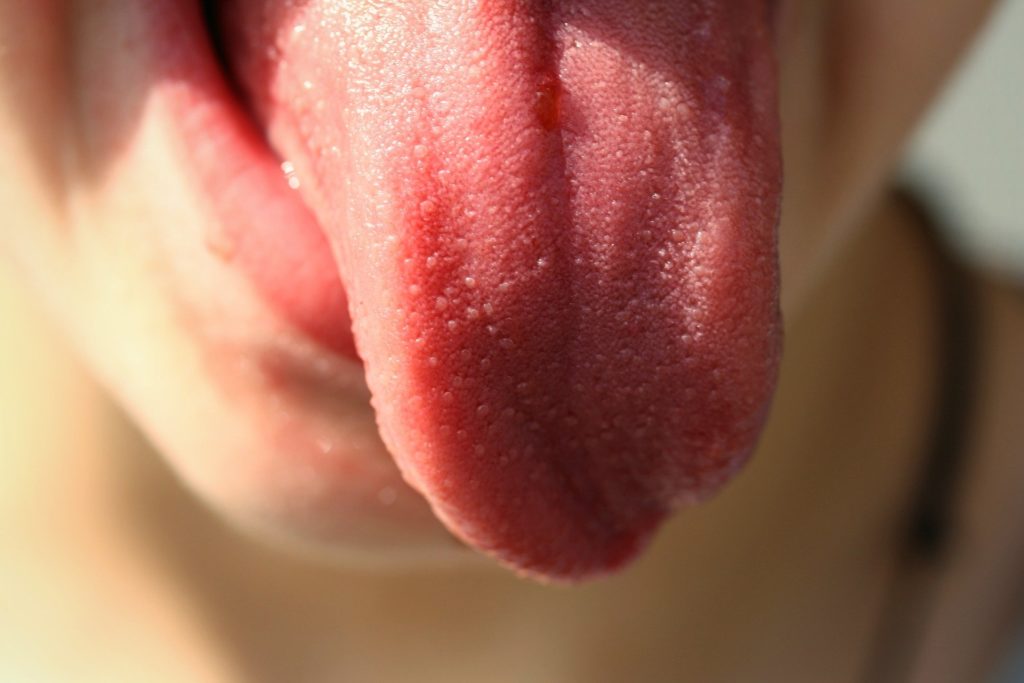
Tongue : The tongue is a voluntary muscular that occupies the floor of the mouth . It is attached by base to the hyoid bone . The tongue contains sensory receptors for the sense of there are 3 varieties of papillae they are:
- Vallate papillae: They and usually between 8-12 and are arranged in an inverted V shaped towards the base of the tongue.
- Fungiform papillae :They are mainly situated at the tip of the tongue and arc numerous in number
- Filiform papillae: They are present on anterior side of the tongue and are smallest and numerous in number.
The main functions of the tongue are mastication, deglutition, speech and taste.
Teeth:There are 32 teeth in the mouth and fixed in their socket in the upper jaw(Maxilla) and the lower jaw (Mandible) they are arranged in curved form.Babies are born with two sets of teeth the deciduous or the temporary teeth and the permanent teeth.
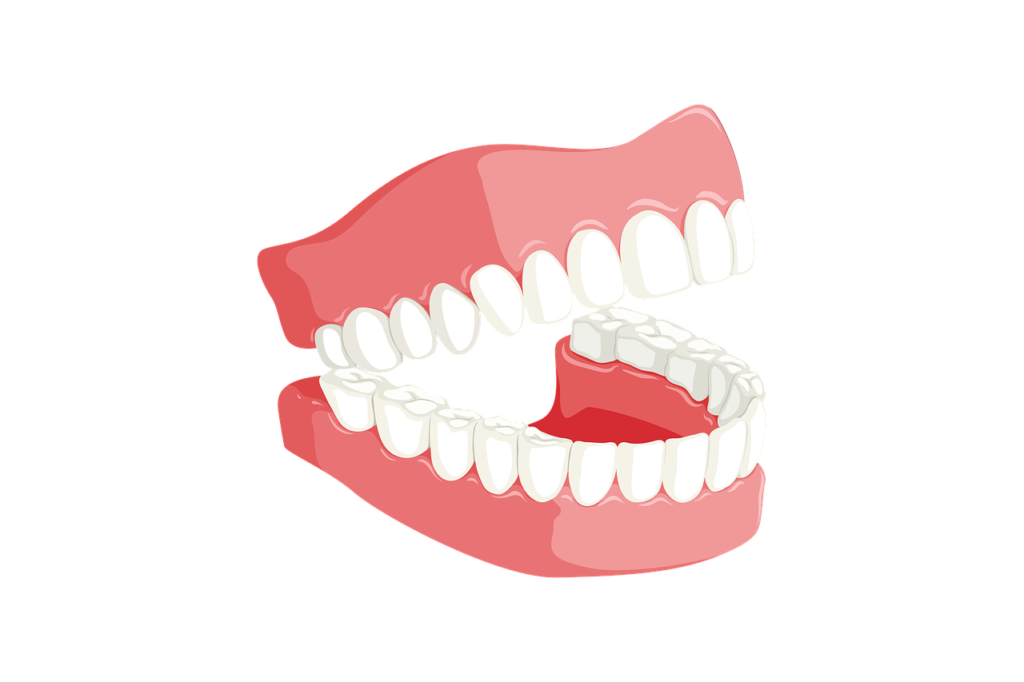
There are 20 temporary teeth, 10 in each jaw and begin to erupt when the child is about 6 months old. The permanent teeth begin to replace the deciduous teeth in the 6th year of age and this dentition, consisting of 32 teeth is usually completed by the 24th year.
It consists of:
- Crown: The part that protrudes from the gum
- Root:the part embedded in the bone
- Neck: the slightly narrowed region where the crowen merges with the root.
In the centre of the tooth there is a pulp containing blood vessels, lymph vessels and nerves, and surrounding this there is hard ivery substance called Dentine. Outside the dentine of the crown is s thin layer of very hard substance called enamel. The root of the tooth is covered by a resembling bone called as cement.
Function of teeth:
The incisors and canine teeth help in cutting and are used for biting off piecea of food. Whereas the premolars and the molar with flat surfaces are used for chewing of food or grinding of food.
pharynx:
The pharynx is divided into three parts they are Nasopharynx, Oropharynx and Laryngopharynx. The Nasopharynx is important in respiration. The oropharynx and Laryngopharynx are common to both respiratory and digestive system. Food passes from the oral cavity into the pharynx and then into oesophagus. Adenoid or tonsils is a lymph node which is present at the back of the Nasopharynx, they help in immune response and trap bacteria.
Oesophagus:
it is a long hollow tube 25 CM in length and 2 cm in diameter. Food passes from the pharynx through the oesophagus and finally pushed into the stomach. The upper and lower ends of the oesophagus are closed by sphincters.
The upper sphincter is known as upper oesophagus sphincter which prevents the air passing into the oesophagus during inspiration.
The lower sphincter is known as cardiac sphincter which prevents the reflux of gastric content into the oesophagus.