Table of Contents
What is nervous system and types of nervous system.
DRUG ACTING ON AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
What is the nervous system?
The nervous system is a complex part of the body that coordinates an animal’s activities and sensory information by sending and receiving signals to and from various parts of the body.
Your nervous system guides almost everything you do, think, say, or feel. It controls complicated processes like movement, thought, and memory.
TYPES OF NERVOUS SYSTEM
Central nervous system (CNS)
•Brain
- Spinal cord
Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
•Sensory nerves
•Motor nerves
•Spinal nerves
Those nerves that transmit information from the body to the CNS are called sensory nerves
Nerves that transmit signals from the brain are called motor nerves
Spinal nerves are mixed nerves that serve both functions.
Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
The Somatic Nervous System
- Motor neurons:
- Sensory neurons:
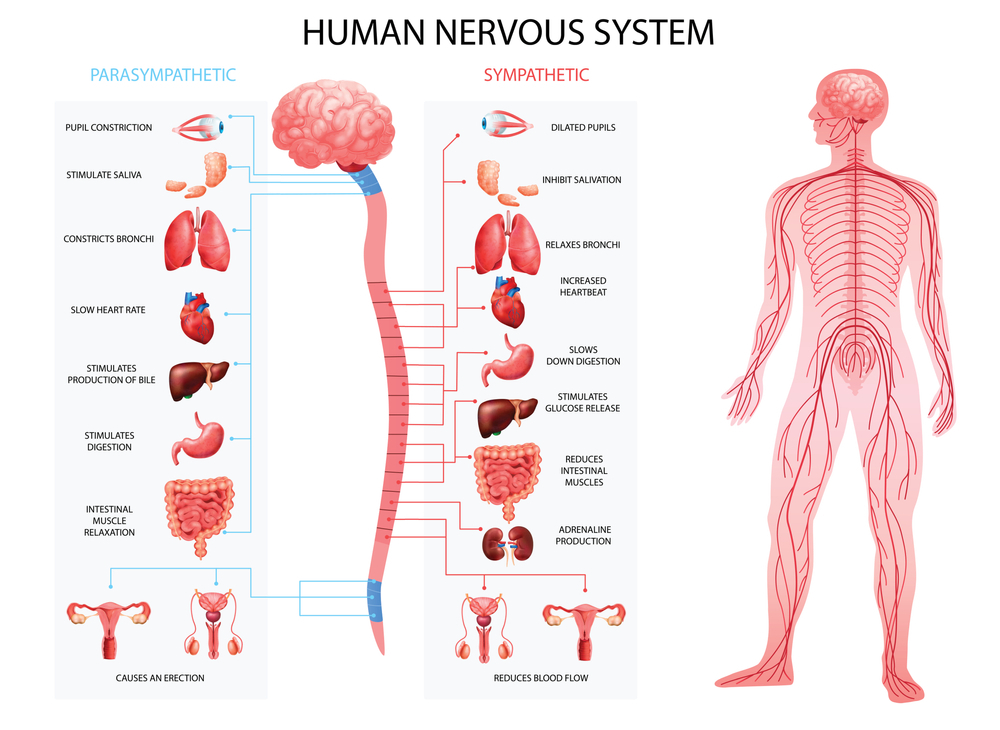
The Autonomic Nervous System
- Parasympathetic system
- Sympathetic system
The somatic system is responsible for transmitting sensory information as well as for voluntary movement.
the peripheral nervous system that’s responsible for regulating involuntary body functions, such as blood flow, heartbeat, digestion, and breathing.
Parasympathetic system: This helps maintain normal body functions and conserve physical resources. Once a threat has passed, this system will slow the heart rate, slow breathing, reduce blood flow to muscles, and constrict the pupils. This allows us to return our bodies to a normal resting state.
Sympathetic system: By regulating the flight-or-fight response,1 the sympathetic system prepares the body to expend energy to respond to environmental threats. When action is needed, the sympathetic system triggers a response by accelerating heart rate, increasing breathing rate, boosting blood flow to muscles, activating sweat secretion, and dilating the pupils.
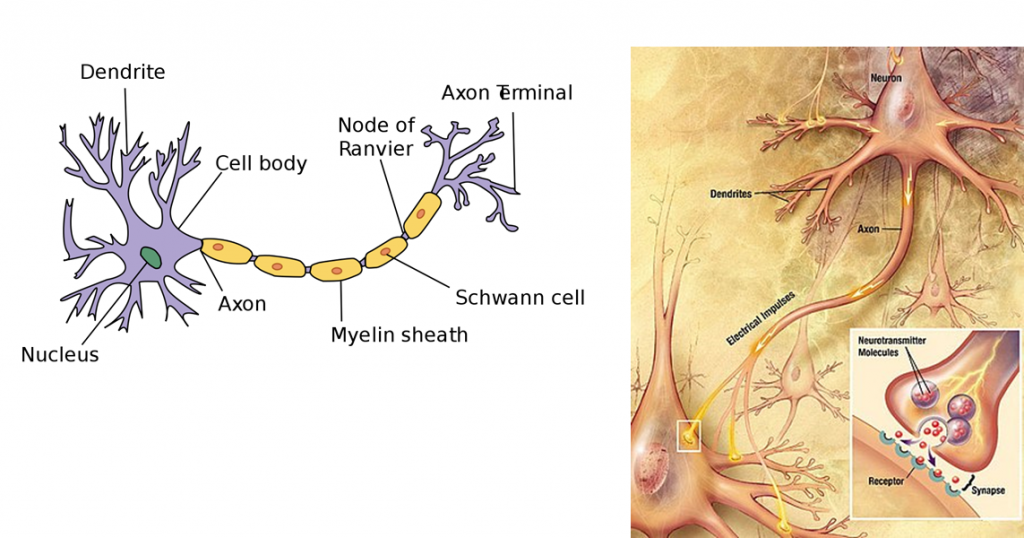
What is neurons?
Neurons (also known as neurons or nerve cells) are the basic components of the brain and nervous system. They are the cells that receive sensory input from the outside world, give motor commands to our muscles, and transform and relay electrical signals at every step along the way.
The chemical messengers of the body are typically referred to as neurotransmitters. They are the chemicals that the nervous system uses to send and receive messages between neurons and between neurons and muscles.
Fortunately, the majority of the work is done by the seven “small molecule” neurotransmitters acetylcholine,
dopamine,
gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA),
glutamate,
histamine,
norepinephrine,
serotonin.