Table of Contents
Structure and uses of aminoglycosides drugs
Aminoglycosides/ aminoglycosides drugs are antibiotics that are mostly used to treat infections caused by aerobic gram-negative bacteria, although they are also effective against other bacteria such as Staphylococci and Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Antibiotics are frequently used in conjunction with them.
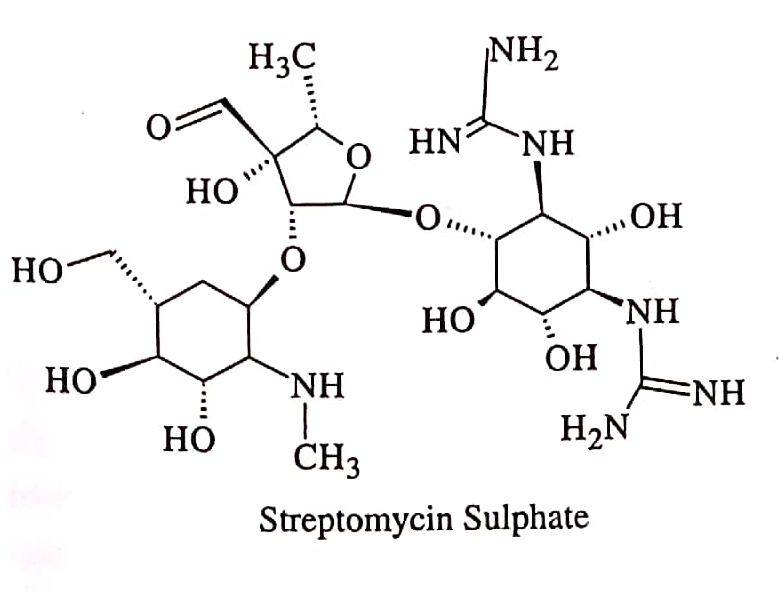
Streptomycin;
Mechanism of action
Aminoglycosides work directly on the bacterial ribosome to prevent protein synthesis from starting. Interfering with ribosomes often causes misreading of the genetic code, resulting in protein synthesis stops.
Uses:
Topically used in the treatment of infected bedsore, pyodermata, burns conditions, and eye infections.
It is used in the treatment of infection caused by gram-negative bacterial.
Gentamycin:

Mechanism of action
Gentamycin binds to 30s ribosomal subunits to form a complex that prevents proper amino acid polymerization, causing protein synthesis to halt.
Uses
It is used to treat Respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections, blood, bone infections, and soft tissue infections.
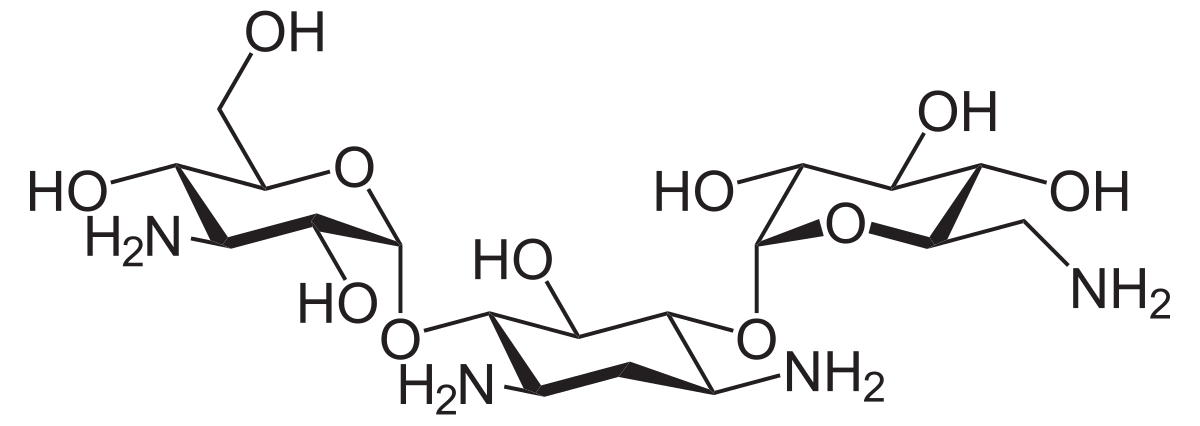
Kanamycin sulfate
Mechanism of action
Kanamycin sulphate binds to 30s ribosomal subunits, forming a complex that is unable to initiate proper amino acid polymerization, causing protein synthesis to halt.
Uses: It is used in the treatment of
- Respiratory tract infection
- urinary tract infection
- blood, bone infections
- soft tissue infections
kanamycin is a useful drug in the treatment against following bacterial infections
- Enterobacter aerogenes
- klebsiella pneumoniae
- serratia marcescens
- acinetobactor species.
Make sure check our Amazing article on: Drug metabolism phase-1 and phase-2 metabolism