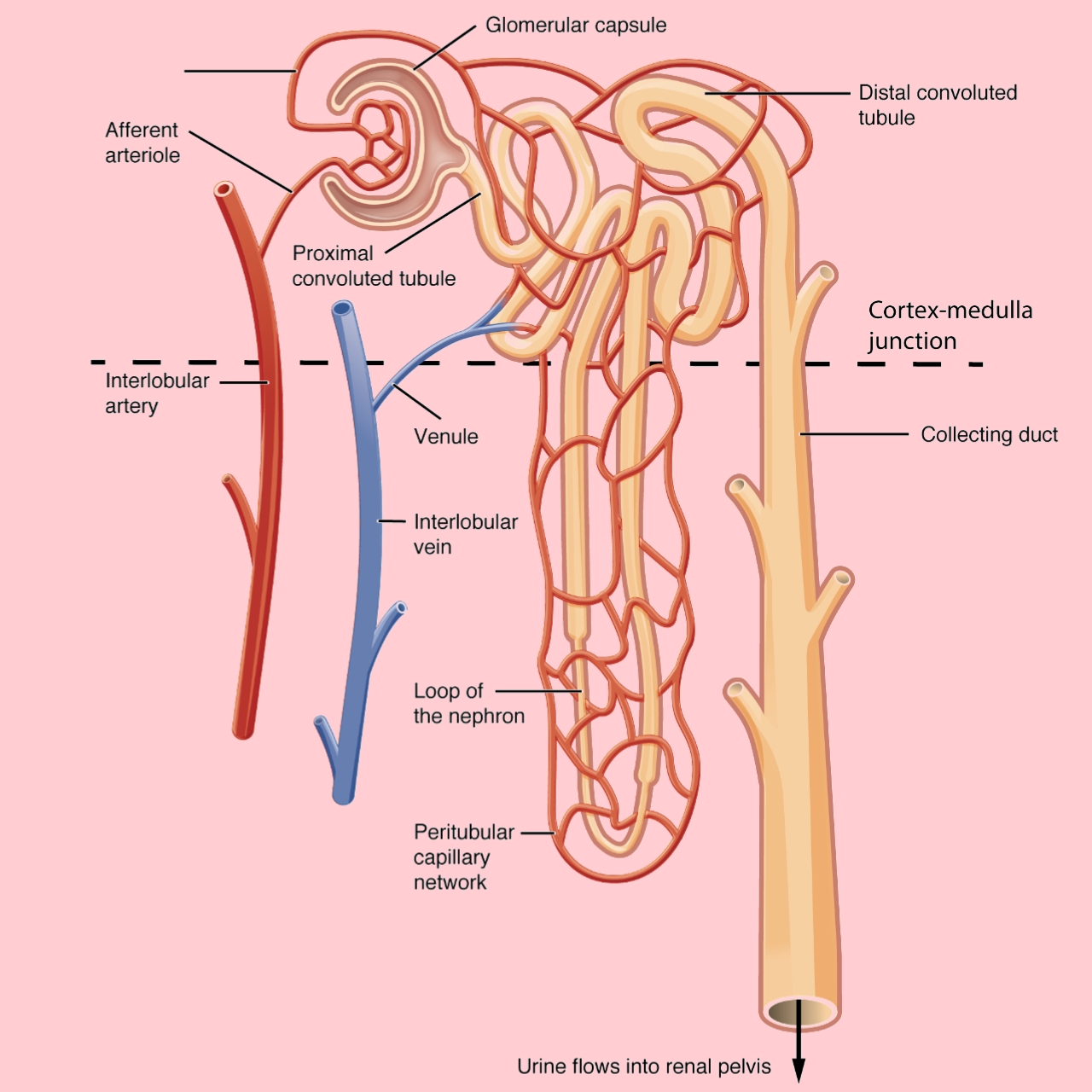
Structural and functional unit of kidney is the nephron and there are about 1 million nephrons in the kidney.
Each nephron consists of

- Bowman’s capsule
- Glomerulus
- Proximal convoluted tubule
- Loop of Henle
- Distal convoluted tubule
- Collecting duct
- Duct of bellini
Bowman’s capsule: The cavity of this capsule is occupied by a network of blood capillaries which collectively from a structure called glomerulus.
Glomerulus: It is a tuft of capillaries with an afferent capillary coming in from the circulation and an enterent capillary going out into the circulation. Glomerus acts as ultra-filter.
proximal convoluted tubule (PCT): It is limed by cubical cells. These cells are active and secrete some enzyme like carbonic-anhydrase which helps in the maintenance of acid base balance in the blood.
Henle’s loops: It is a U-shaped tube and has a descending limb and ascending limb. Loop of Henle is physiologically important because it reabsorbs a number of important substances that are filtered by the glomerulus into the blood.
Distal convoluted Tubule: These are limb by cuboidal cell. The absorption of Na+ is under the control of aldosterone which takes place in this part of nephron.
Collecting duct: They are lined by cuboidal cells. Collecting tubules of nephron unite together to form one straight tube.
Duct of Bellini: This arises from the final combination of many straight tubules and finally drains into apex of the pyramid of the kidney.