Table of Contents
Inflammation
Inflammation is defined as” the local response of living mammalian tissues to injury due to any agent”. It’s a body defense reaction in order to eliminate or limit the spread of injuries agent, followed by removal of the Necrosis cell and tissues.
Mechanism of inflammation
Acute inflammation is characterized by vasodilatation, fluid exudation, and neutrophil infiltration. These processes are activated and amplified by a series of intracellular and extracellular factors that tightly coordinate the inflammatory process. The innate immune system responds rapidly to infection or injury.
Inflammation is a protective response that is intended to limit or eliminate the initial cause of cell injury and along with the removal of dead and necrotic cells.
Etiology of Inflammation
- Physical Agents: Heat cold radiation
- Chemical Agents: Organic and Inorganic poison
- Infective Agents: Bacteria, virus and their toxins
- Immunological agent: cell mediated and Antigen Antibody reaction.
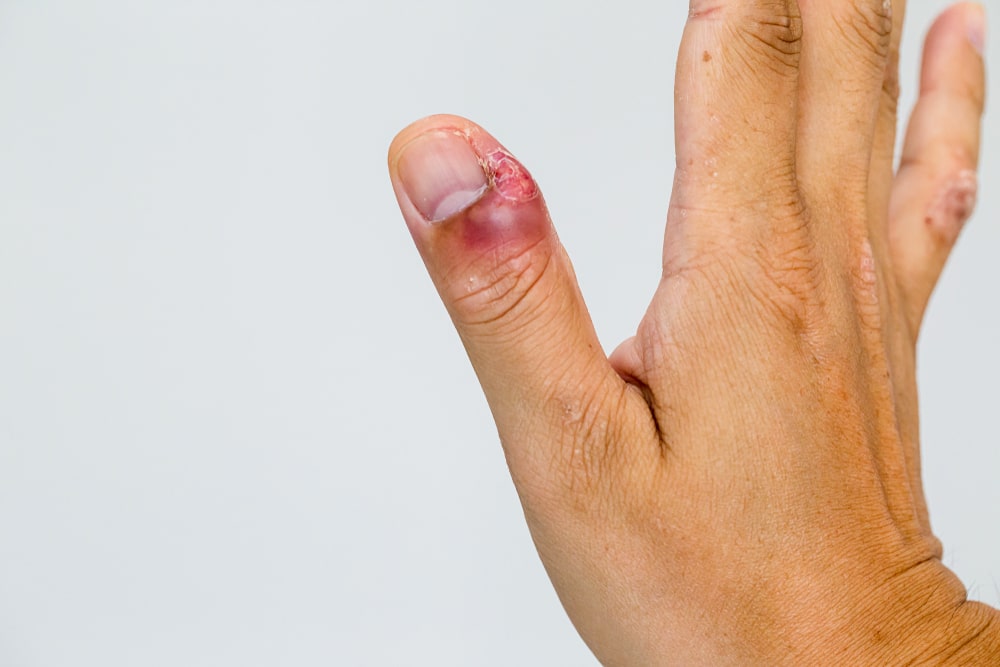
Clinical signs of Inflammation
There are four signs of inflammation which are also called cardinal signs of inflammation.
- Rubor ————Redness
- Tumor————-Swelling
- Calor—————- Heat
- Dolar————— Pain
- Rubor: This is Latin term for ‘Redness’, This is because of capillaries are filled with more amount of blood than normal.
- Tumor: Latin term for ‘swelling‘ it caused by accumulation of fluid.
- Calor: Latin term for heat. It’s reson for the redness more blood in the affected area makes it feel hot to the touch.
- Dolor: Latin term for pain chemical that stimulates nerve endings are released making the area much more sensitive.