Table of Contents
Introduction
Innate Immunity: The body is protected from infection by anatomic and physiologic barriers in the skin and the respiratory, intestinal, and urogenital tracts. If these barriers are breached an innate immune response is generated. In the response, phagocytic cells, antimicrobial proteins, and serum enzymes are activated by molecules common to most bacteria. The innate immune response functions to contain an infection until an adaptive response can be mounted against the infective agent. An adaptive response begins 7 to 10 days after infection and consists of antibodies, CD4Th1 inflammatory response, or CD8 cytotoxic cells.
Anatomic and physiologic barriers
Skin The skin is an inhospitable environment for bacterial colonization and growth except for Staphylococcus epidermidis, bacteria cannot attach to the outer layer of skin or stratum corneum because it is composed of dead keratinocytes, keratin, ceramides, free fatty acid, and cholesterol. Moreover, the stratum corneum is continually shed and renewed by younger keratinocytes pushing up from below. Bacterial colonization is prevented by other factors as well. Perspiration deposits salt on the skin. High salt concentrations create a hypertonic environment that inhibits bacterial growth. Sebaceous glands also produce a wax-like substance called sebum, which contains lactic acid and propionic acid produced by Propionibacterium acnes—a commensal organism found in the sebaceous gland. Sebum reduces the skin pH to between 3.0 and 5.0, and this acidic environment inhibits bacterial growth.
Respiratory Tract
The respiratory tract is protected from infection by ciliated epithelial cells and a mucous layer. Glycosylated mucous proteins cover the entire respiratory tract and trap particulate matter. The coordinated beating of the cilia on respiratory epithelial cilia moves the mucus upward to the glottis, where it is expelled from the airways or swallowed. This mechanism is referred to as the mucociliary escalator. The mucous covering is replaced several times each day, leading to the production of a pint to a quart of mucus per day. Defective escalator function increases the risk of developing respiratory tract infections, sinusitis, and otitis media. Mucociliary escalator dysfunction can be inherited or can be the result of environmental insults. For example, primary ciliary dyskinesia (PCD) is an inherited syndrome characterized by impaired transport and the abnormal structure of cilia. In this syndrome, lungs and sinuses are prone to repeated infections. Environmental insults and drugs often affect the function of the mucociliary escalator. For example, halothane, cocaine, and sulfur dioxide are toxic to epithelial cells. Smoking or inhalation of toxic fumes also injures the epithelium causing loss of ciliated cells. Escalator function can be compromised by cold or dry air that often creates a highly viscous mucus that cannot be moved upward by ciliated cells.
Stomach and Intestine
Stomach acid forms a passive barrier to prevent infection of the intestinal tract. Except for Helicobacter pylori (the etiologic agent of gastric and duodenal ulcers), most ingested pathogenic bacteria cannot survive in stomach acid. Bile salts found in the intestine also are toxic to bacteria.
Urogenital Tract
The components of the urogenital tract that actively participate in the innate immune response are the urethra and the vaginal mucosa. The urethra is usually sterile because the persistent flushing of urine prevents bacterial attachment to urethral epithelial cells. The acidity of urine also prevents bacterial colonization. In females, the normal flora of the vaginal mucosa prevents colonization by pathogenic microbes. Acids produced by lactobacilli create a slightly acidic mucosal environment that inhibits bacterial growth. The risk of infection increases when the lactobacillus population is reduced, the pH of urine is increased, or both.
Pathogen-associated molecular patterns
Pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) are molecular structures or molecules that are shared by most pathogenic bacteria and some viruses. Most components are constituents of microbial cell walls, single-stranded and double-stranded nucleic acids, or unmethylated deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Common PAMPs are presented in Table 2-1. In an innate immune response, PAMPs are recognized by several different mechanisms, including the following: • Serum complement components • Receptors on leukocytes and tissue cells • Acute phase proteins
Serum complement components and pathogen-associated molecular patterns
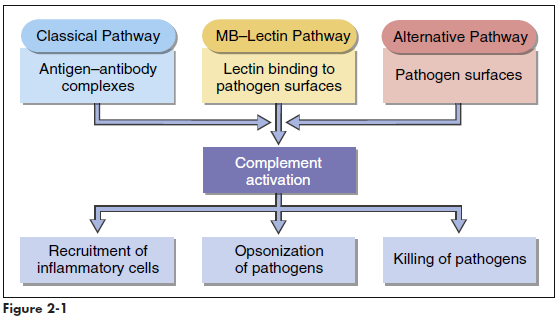
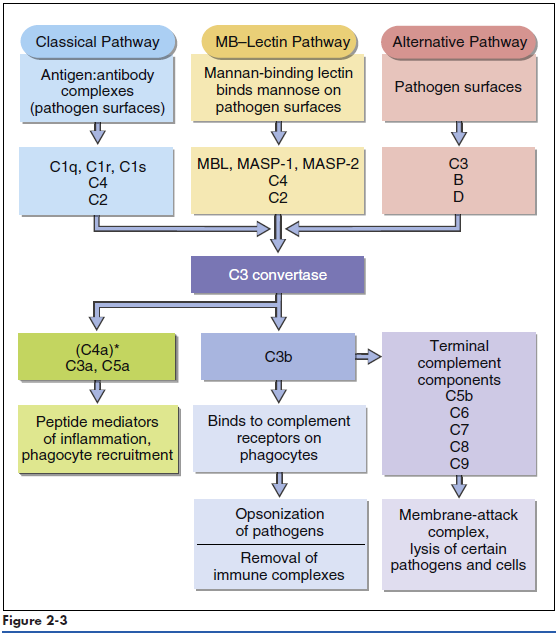
Complement comprises nine serum proteins (Figure 2-1) and produces proinflammatory factors that are chemotactic for phagocytic cells. Complement fragments coat bacteria to create opsonins, which are, by definition, molecules that attach to microbes and promote phagocytosis. Complement can be activated by different mechanisms. In an adaptive response, complement is activated by antigen-antibody complexes. Three other mechanisms do not require the presence of antibodies and are activated during an innate immune response. Complement can be activated by interaction with select molecules (e.g., zymozan) on microbial surfaces in an alternative complement activation pathway. Lectins (proteins that bind to sugars) also activate the complement cascade in the mannose-binding lectin (MBL) pathway. Some acute phase proteins produced by the liver during inflammation activate the complement cascade (see Acute Phase Response).
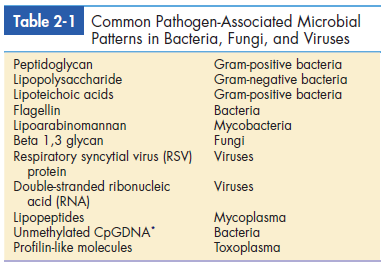
phosphate guanine motifs.
Mannose-binding Lectin Complement Activation Pathway
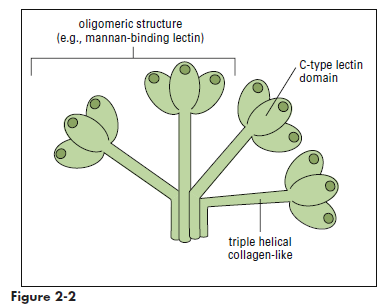
Collectins are a family of lectins that react with terminal mannose or fructose molecules on microbes and activate complement. The collectin family includes Mannose-binding lectin (MBL), bovine conglutinin, lung surfactants A and D, and bovine collectin 43. Structurally, collectins are multimeric proteins with a “flower bouquet” or an “X-like” structure (Figure 2-2). MBL is the most studied of the collectins. MBL circulates in a complex with MBL-associated serine protease 1 and 2 (MASP1 and MASP2). In the presence of calcium, MBL or MASP binds to PAMPs such as N-acetylglucosamine, mannose, and N-acetylmannosamine residues expressed on bacteria, fungi, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), and influenza virus. Following an initial interaction with target molecules, the serum complement cascade is activated. MBL or MASP activates the C2 and C4 complement components to create a C3 convertase (Figure 2-3). Cascade fragment C3b binds to bacterial PAMPs and acts as an opsonin. Other complement fragments such as C3a and C5a induce the release of histamine and pharmacologic mediators from mast cells and basophils. These fragments are called anaphylatoxins. Histamine increases capillary permeability and fluid leaks into tissue. Fluid leaking from capillaries reduces fluid levels in the vessels and precipitates bacteria, rendering them more susceptible to phagocytosis. In addition to their role as anaphylatoxins, C3a and C5a are chemoattractants for phagocytic cells. Complexes of C5b, C6, and C7-C9 create a membrane attack complex that inserts a “tube-like” structure through the bacterial membrane, which results in the death of the bacterium.
Receptor Recognition of Pathogen-Associated Molecular Patterns
Phagocytic cells have a number of receptors that recognize PAMPs on pathogenic microbes. Scavenger, carbohydrate, and Toll-like receptors are important in the recognition of PAMPs. Scavenger receptors bind lipoteichoic acids, endotoxins from gram-negative bacteria, and peptidoglycans from gram-positive bacteria. Carbohydrate receptors recognize mannose or fructose in the terminal sugars of bacterial glycoproteins (Figure 2-4). Toll-like receptors (TLRs) present on lymphocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells play a more important role in innate immunity. The 11 different TLRs in mammals usually recognize only one type of PAMP (Table 2-2). For example, TLR-2 binds to the peptidoglycans of Streptococcus and Staphylococcus, whereas TLR-5 only binds to the proteins of bacterial flagellae. The ligands for TLR receptors are listed in (Table 2-3). Interactions between the PAMP and its receptor activate intracellular signaling and the synthesis of specific small-molecular-weight messengers called cytokines that activate both the innate immune system and the adaptive immune system.
domains
Receptor activation and functional responses in innate immunity
The ligation of PAMPs with Toll-like receptors accelerates the phagocytosis of microbes. During phagocytosis, the cell membrane envelopes bacteria and creates an intracellular vacuole called a phagosome. Primary granules fuse with the phagosome to create a phagolysosome. Enzymes in the granule kill the microbes by breaking their cell walls and disrupting membrane function (Figure 2-5). At the same time, the oxygen-dependent killing mechanism produces singlet oxygen, hydrogen peroxide, and hypochlorous acid. These substances, along with nitric oxide, are released into the phagolysosome to kill bacteria. Interactions between PAMPs and Toll-like receptors on macrophages cause the release of interleukin 6 and interleukin 12 (IL-6 and IL-12) from phagocytic cells. IL-6 plays a role in the proliferation of CD8 cytotoxic T cells. It also upregulates adhesion factors on endothelial cells, which allows the egress of phagocytic cells and lymphocytes from the vasculature. IL-6 may also play a role in autoimmune reactions.
Toll-Like Receptors and Autoimmunity
The ligation of Toll-like receptors and the production of IL-6 result in the inactivation of regulatory cells that control the autoimmune B cells in peripheral blood. The disruption of the regulatory network allows B cells to produce autoantibodies directed at host tissue. For example, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune response that is characterized by autoantibodies directed at DNA. The disease is exacerbated by the recognition of cytosine- and guanosine-containing unmethylated DNA by TLR-9 receptors on leukocytes and the release of IL-6.
Toll-Like Receptors, Endotoxins, and SepticShock
Lipopolysaccharide endotoxins are biologically important PAMPs. Endotoxins, which are an integral part of the gram-negative cell wall, are released on the death of the bacterium and react with CD14 and TLR-4 receptors on the macrophage surface. Intracellular signaling induces the synthesis and release of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1, IL-2, IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-α [tumor necrosis factor–alpha]). TNF-α is the central cytokine involved in septic shock syndrome. Manifestations of septic shock include tachycardia, tachypnea, alterations in temperature, and activation of the coagulation cascade. Arterial and venous dilation results in septic shock. As a consequence of hypovolemia, tissue perfusion becomes inadequate, which results in cellular dysfunction. The mortality rate among patients with septic shock ranges from 20% to 80%.
Acute-phase response
In innate immunity, mammals respond to tissue injury or infection by initiating an acute phase response. The response is characterized by fever, emargination of polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs), and the synthesis of acute-phase proteins by the liver. Acute-phase proteins inhibit bacterial growth or activate the complement cascade. The most common acute-phase proteins are listed in Table 2-3. During the response, white blood cells also produce a wide variety of antimicrobial agents such as cathelicidins, defensins, and nitric oxide.
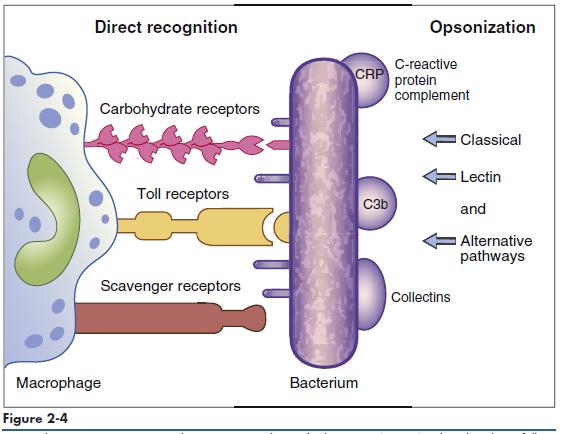
opsonization with serum molecules.
Temperature
Most pathogenic bacteria have a narrow growth range at temperatures between 96°F and 100°F. An elevation in body temperature or fever slows bacterial replication until an adaptive immune response can be generated. Fever is induced by IL-1 and Interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) released by monocytes. The interleukins travel to the hypothalamus and increase the temperature set point. Since these cytokines can regulate temperature, they are termed endogenous pyrogens. Other cytokines (anti-pyretic) such as IL-10 and TNF-α modulate and maintain the temperature response.
Acute Phase Proteins
C-reactive protein (CRP), the most studied acute-phase protein (see Table 2-3), activates the complement cascade. Cleavage of other complement components creates opsonins that bind to microbial PAMPs and promotes phagocytosis. Other acute-phase proteins such as ferritin, haptoglobin, and ceruloplasmin bind or oxidize free iron in serum to prevent microbial growth. Iron is necessary for the synthesis of cytochromes and the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
Antimicrobial Agents Produced by Cells andTissues
Cathelicidins
Cathelicidins are proteins produced by the PMNs, keratinocytes, and epithelial cells of the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts. Cathelicidin subsets have different biologic functions. PMN-produced cathelicidins have broad-spectrum microbial toxicity. Other cathelicidins synthesized by epithelial cells bind and neutralize lipopolysaccharide endotoxins. In the skin, keratinocyte cathelicidins are chemotactic for phagocytes and T cells. Animal studies show that cathelicidins are important in host defense against Group A streptococci that cause necrotic skin lesions.
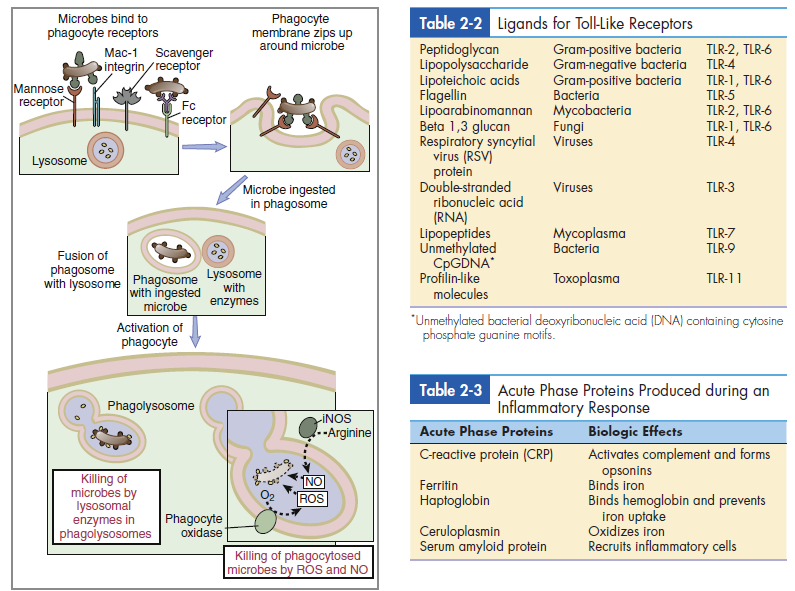
neutrophils express many surface receptors that may bind microbes
for subsequent phagocytosis; selected examples of such receptors are
shown.
Defensins
Defensins are small (29–35 amino acids) proteins produced by circulating white blood cells and tissue cells. Defensins can be classified into alpha and beta families. Alpha-defensins (α-defensins) are found in neutrophils, macrophages, and Paneth cells in the intestine. Paneth cell defensins are called crypticidins and serve to reduce the number of bacteria in the intestinal lumen. Beta-defensins (β-defensins) are secreted by most leukocytes and epithelial cells. Defensins have broad-spectrum activity against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria and kill bacteria in some ways. Some defensins create voltage-dependent channels in bacterial membranes that allow the influx of water. Increased osmotic pressure ruptures the bacterial membranes. Other defensins move through bacterial cell walls, bind to target cells, and disrupt normal metabolism. A specific β-defensin called a tracheal antimicrobial peptide (TAP) is found along the entire length of conducting airways. In the lung, the β-1 TAP defensin prevents infection by virulent or opportunistic pathogens. In patients with cystic fibrosis (CF), the TAP is inactivated by high salt concentrations in the respiratory mucosa. This allows the development of respiratory tract infections with opportunistic pathogens such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Defensins also prevent the influenza virus from entering target cells. Influenza hemagglutinins are necessary for binding the virus to the target cell. Defensins render the virus non-infectious by cross-linking hemagglutinins, which prevents the normal interaction between the virus and the host cell membrane.
Nitric Oxide
Nitric oxide is a highly reactive molecule produced by macrophages following interactions between Toll-like receptors and PAMPs. In a chemical reaction, nitric oxide synthase oxidizes L-arginine to L-citrulline and nitric oxide (NO). Exposure to NO is cytotoxic to bacteria, fungi, parasites, and tumor cells. Toxicity is related to NO’s ability to inhibit DNA synthesis mitochondrial respiration. Prolonged NO generation can be detrimental to the body. Chemical reactions between NO and oxygen (O2) forms dinitrogen trioxide in mammalian cell membranes and disrupt normal cellular function.
Pathogen-associated microbial patterns and vaccines
PAMPs are being considered as additional components of vaccines because they stimulate both the innate and the adaptive immune systems. When added to vaccines, compounds that stimulate and direct the immune response are termed adjuvants. Adjuvants work by reducing antigen solubility and releasing small amounts of antigens over an extended period. PAMPs are used adjuvants. A purified PAMP from the tuberculosis bacterium called muramyl dipeptide is used in Freund’s complete adjuvant to induce a cell-mediated immune response to antigens.
Immunodeficiency and innate immunity
Most individuals with an MBL deficiency are healthy, but an increased incidence of otitis media, chronic upper respiratory tract infections, chronic diarrhea, and autoimmunity are seen among them. In infants, MBL may play an important role in the transition from passive immunity from the mother to mature adaptive immune responses.
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on : Cells and Organs of the Immune System