Homeostatic imbalance
Homeostatic imbalance: This occurs when an internal environmental factor’s level deviates from its normal range due to insufficient fine control. If homeostasis cannot be maintained under control, an aberrant state emerges that could endanger one’s health or even life.
In the study of anatomy and physiology, the body systems are traditionally described individually, although in actuality, they are all interrelated. This section introduces body functions and how they relate to demands for survival, as depicted in the diagram below.
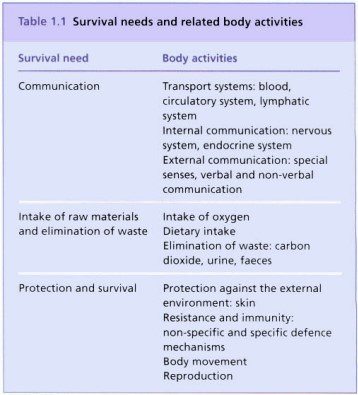
Communication
Transport and communication are discussed in this section. All cells have access to both their internal and exterior environments thanks to transport systems; these systems include the lymphatic, circulatory, and blood systems. Receiving, compiling, and responding to pertinent information is a requirement for any communication system.
The internal and external environments can be communicated with through various systems. The neurological and endocrine systems, which are crucial to maintaining homeostasis and regulating essential bodily processes, are primarily involved in internal communication. Special senses, linguistic and nonverbal behaviors, and all of these depend on the nervous system in order to communicate with the outside world.
Also read: Definition of homeostasis