What is Emulsion?
The emulsion is a biphasic liquid preparation containing two immiscible liquids, one of which is dispersed as minute globules into the other. The liquid which is converted into minute globules is called the ‘dispersed phase’ and the liquid in which the globules are dispersed is called the ‘continuous phase’.
Preparation of Emulsions
The following methods are commonly used for the preparation of emulsions on a small scale:
- Dry gum method
- Wet gum method
- Bottle method
- Other methods
- Dry Grum Method:
- i) Measure the required quantity of oil in a dry measure and transfer it into a dry mortar.
- ii) Add the calculated quantity of gum acacia into it and triturate rapidly so as to form a uniform mixture.
- iii) Add the required quantity of water and triturate vigorously till a clicking sound is produced and the product becomes white or nearly white due to the total internal reflection of light. The emulsion produced at this stage is known as a primary emulsion.
- iv) Add more water to produce the required volume.
The following table shows the proportion of oil, water, and gum acacia required for different types of oils:
| S.No | Type of the Oil | Examples | Ratio of Oil:Water:Gum |
| 1. | Fixed oil | Castor oil Almond oil Arachis oil Cod-liver oil Turpentine oil | 4:2:1 |
| 2. | Volatile oil | Peppermint oil Cinnamon oil | 2:2:1 |
| 3. | Mineral oil | Liquid paraffin | 3:2:1 |
2. Wet Gum Method: In this the proportion of oil:water: gum for preparing the primary emulsion is the same as given in the table.
- i) Calculate the quantity of oil, water, and gum required for preparing the primary emulsion.
- ii) Powder the gum acacia in a mortar. Add water and triturate it with gum so as to form mucilage.
- iii) Add the required quantity of oil in small portions with rapid trituration until a clicking sound is produced and the product becomes white or nearly white. At this stage, an emulsion is known as a primary emulsion.
- iv) Add more of water in small portions to the primary emulsion with trituration to produce the required volume. Stir thoroughly so as to form a uniform emulsion.
- v) Transfer the emulsion to a bottle, cork, label, and dispense
3. Bottle Method: The bottle method is used for the preparation of emulsions of volatile and other non-viscous oils. The proportion of oil:water:gum is 2:2:1.
- i) Measure the required quantity of the oil and transfer it into a large bottle. Add the required quantity of powdered gum acacia.
- ii) Shake the bottle vigorously, until the oil and gum are mixed thoroughly.
- iii) Add the calculated amount of water all at once.
- iv) Shake the mixture vigorously to form a primary emulsion.
- v) Add more of water in small portions with constant agitation to produce the required volume.
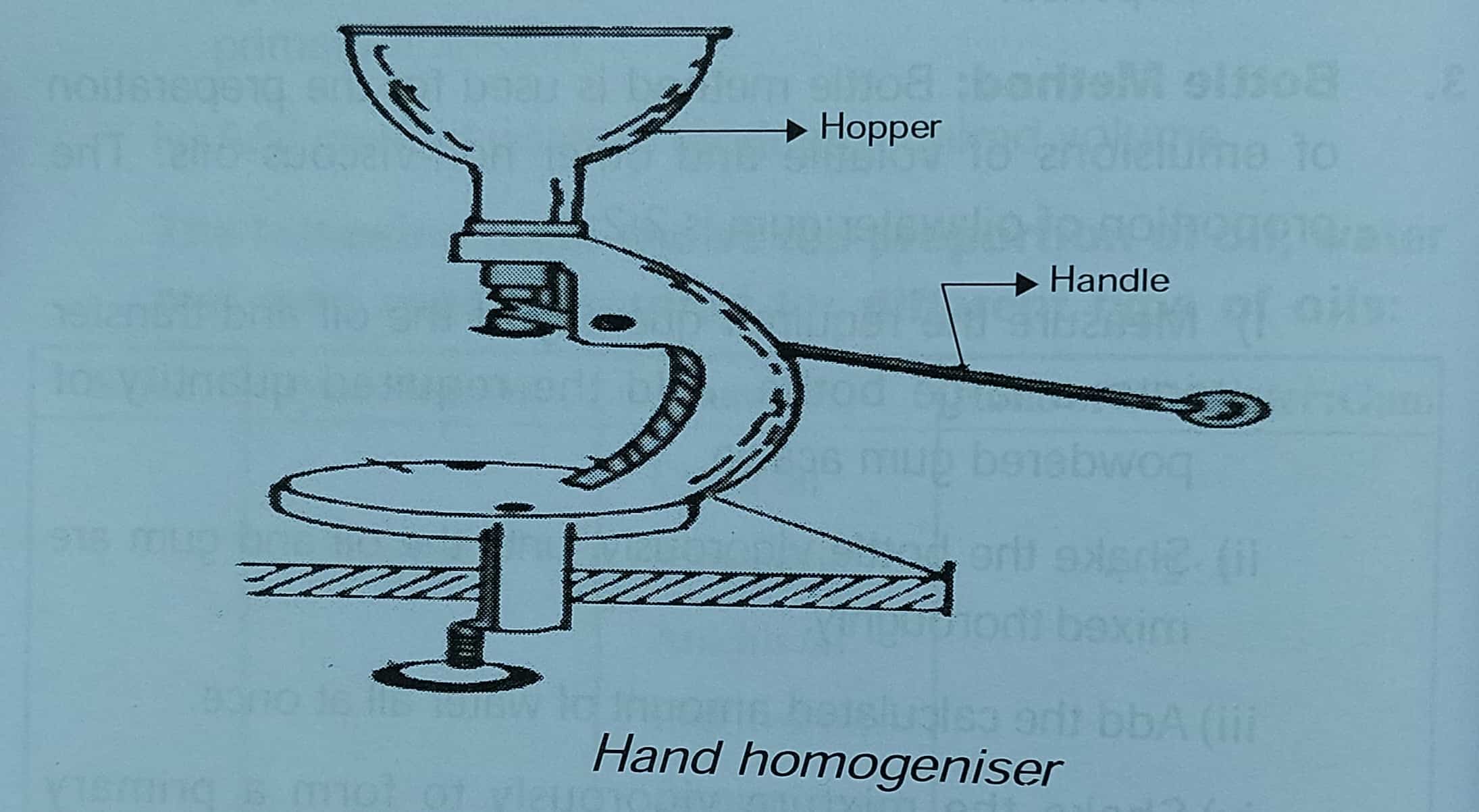
4. Other Methods: Various blenders and homogenizers are used for preparing emulsions. Hand homogenizer, Silverson mixer homogenizer, and colloidal mill are some of the homogenizers which are used for the preparation of extemporaneous emulsions. These homogenizers are based on the principle that the large globules in coarse emulsion are broken into smaller globules by passing them under pressure through a narrow orifice.
a) Hand Homogeniser: The homogenizer is hand-operated and the coarse emulsion is passed through a fine orifice. The emulsion is placed in the hopper of the homogenizer. The up-and-down movement of the handle causes the coarse emulsion to draw in through inlet value and pass through homogenizing value. In this way, the emulsion is forced to pass through the fine orifice. The oil globules are broken into fine globules of uniform size.
Also read: What is solution