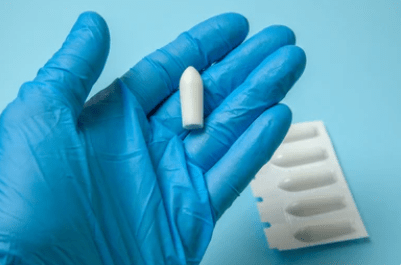
Suppositories: “Suppositories are semisolid dosage forms of a medicament for insertion into body cavities other than mouth”.
- Rectal suppositories – They are meant for introduction into the rectum for systemic effects.
- Vaginal suppositories – They are also called pessaries. They are used in vagina for local effects.
- Nasal suppositories-They are also called nasal balgies used in the nasal cavity.
- Urethral suppositories-These are also called urethral bougres used in urethra.
- Ear cones suppositories – These are also called as aurinaria are rarely used.
Table of Contents
Preparation of suppositories
Suppositories are prepared by the following methods
- Rolling method.
- Hot process or fusion method.
- Cold compression method.
Rolling method: It is an ancient method of preparing suppositories. The suppository base is rolled and then the desired shape is given with the hand. This is not used nowadays.
Hot process or fusion method: This method is used for preparation of suppositories for dispensing purposes. The suppository base is melted, the medicament is incorporated and base is adjusted using the displacement values. Then it is filled in the mould. On cooling, suppositories are formed which are removed from the mould. Prior to this the mould is cleaned and lubricated by the use of liquid paraffin.
Method of preparation suppositories:
- Thoroughly clean and lubricate the mould with a suitable lubricant. Keep it on ice in the inverted position to cool and drain an excess of the lubricant. The lubrication of the mould is not required in case the emulsifying base or synthetic base is used.
- Heat the china dish over a water bath. To this add the required quantity of cocoa butter or any other base after taking into account the displacement value of the medicament. Allowance is made for unavoidable wastage during preparation by calculating two extra suppositories.
- Remove the china dish from the water bath, when two-thirds of the base melts and stir thoroughly until whole of the mass melts. The process prevents overheating of the base.
- Place the weighed quantity of powedered medicament to be incorporated with the suppository base on an ointment tile. Pour about half of the melted base over it. Mix it thoroughly with a flexible spatula. Transfer the mixed mass to the china dish and mix thoroughly so that a homogenous mass is formed.
- Warm the china dish over a water bath for a new second with constant stirring, so that mass becomes pourable.
- Pour the melted mass into the cavities of the suppository mould, kept over the ice. Fill each cavity to overflowing, in order to prevent the formation of hollows in the tops of the finished suppositories because cocoa butter contracts on cooling and hollows are formed at the top of the suppositories. Precautions must be taken while pouring the mass into the cavities. It must be continuously stirred to ensure even distribution of the medicament in all the suppositories.
- Remove the excess of mass with the help of a sharp knife or blade when the mass is properly set.
- Keep the mould over ice or in a cool place for 10 to 15 minutes.
- Open the mould and remove the suppositories.
- Wipe off the suppository lightly with a clean or filter
- Wrap the individual suppository in wax paper.
Cold compression method: This method is useful for themolabile and insoluble drugs because heating and stirring of the base with medicament are not required. Cocoa butter is grated and ingredients are mixed with it. The remaining amount of grated cocoa butter is added and the mass is allowed for compression. Compression of the prepared mass is done on hand or power-operated compression machines. This method is not suitable for glycerogelatin bases or any other base in which melting is required.
Classification of suppository bases
Suppositories are solid dosage forms of a medicament for insertion into body cavities other than the mouth. They may be inserted into the rectum, vagina or nasal cavity. Suppositories are available in different shapes, sizes, and weights. Suppositories are used to produce local, systemic, and mechanical action.
Suppository Bases: These are used to prepare suppositories to retain its shape and firmness during storage and administration.
Classification :
1. Fatty Bases :
a) Theobroma Oil: It’s a yellowish white solid obtained from crushed and roasted seeds of theobroma cocca. It’s also known as cocoa butter. It melts at body temp and release the medicament for rapid absorption. It’s considered a most suitable base for rectal suppositories. It’s readily liquify on warming and quickly settle on cooling.
Disadvantages:
- It shows the phenomenon of polymorphism.
- It becomes rancid and melts in warm weather.
- It has a tendency to stick to the sides of the mould when solidified. The leakage from the body cavity on melting can take place.
- It’s expensive
- It’s immiscible with body fluids.
(b) Emulsifeid theobroma oil This may be used as a base when large quantities of aqueous solutions are to be incorporated.
(c) Hydrogenated Oils: These are obtained by hydrogenation of various vegetable oils such as aractis oil, cotton seed oil, coconut oil, palm oil. It’s used as a substitute for theobroma oil because it has a number of advantages our theobroma oil. These are: They are resistant to oxidation They produce colorless, odourless, and elegant suppositories. The emulsifying and water-absorbing capacities are good.
2. Water Soluble and water-miscible bases:
a) Glycero gelatin base: It’s a mixture of glycerin and water which is made stiff by the addition of gelatin. The base may be used for preparing all types of suppositories but its particularly used for making pessaries. The suppositories prepared from glycero- gelatinbase are translucent which tend to dissolve or disperse slowly in the body can’t and relase medicament.
b) Soap Glycerine suppositories: In glycero- gelatin base, the gelatin is replaced with either curd soap or sodium stearate.
c) Polyethylene glycols: These polymers are known as carbowaxes or polyglycors or macrogols, having molecular weight less than 1000 are liquids and higher than 1000 are wax-like solids.
3. Emulsifying bases:
These are synthetic bases.
a) Witepsol: They consist of triglycerides of saturated vegetable acid with a percentage of partial esters. The Suppositories prepared with witepsol should not be cooled. The mould should be lubricated.
b) Massa estarinum : It’s a mixture of mono
c) Massuppol: It consists of glyceryl esters mainly lauric acid small amount of glyceryl monostearate.
Advantages over theobroma oil:
- They solidify rapidly
- They are non-irritant
- Lubrication of mould is not required.
- Overheating doesn’t affect physical properties of the base.
Also, read: Method of preparation of paste