DEFINITION: Hospital pharmacy is defined as actual practice of pharmacy in a hospital. In this department the drugs are procured, preserved, stored, compounded, assayed, manufactured, dispensed, packed and distributed to inpatients and outpatients by professionally compititent and legally qualified pharmacists. Here pharmacist’s advice patients, physicians and other health care professionals on selection of doses, drug adverse effects and drug interactions.
OBJECTIVES:
a) To provide an effective pharmaceutical and clinical services in an organized manner.
b) To ensure availability of right medication, at right time, in right dose at minimum
possible cost.
c) To promote the understanding of hospital pharmacy practice by public, government, industry, and other health care professionals.
d) To conduct pharmaceutical research of scientific, clinical or administrative nature with motto of improving pharmaceutical care and the profession.
e) To participate discuss and implement the decision taken by the P&T committee.
f) To establish drug information centre to provide necessary information to physicians, nurses, or any other professionally competent persons in dealing drugs.
g) To manufacture drugs that are used in critical conditions by the patients that is not readily available from drug manufacturing companies.
h) To interact, cooperate and coordinate with various departments of the hospital.
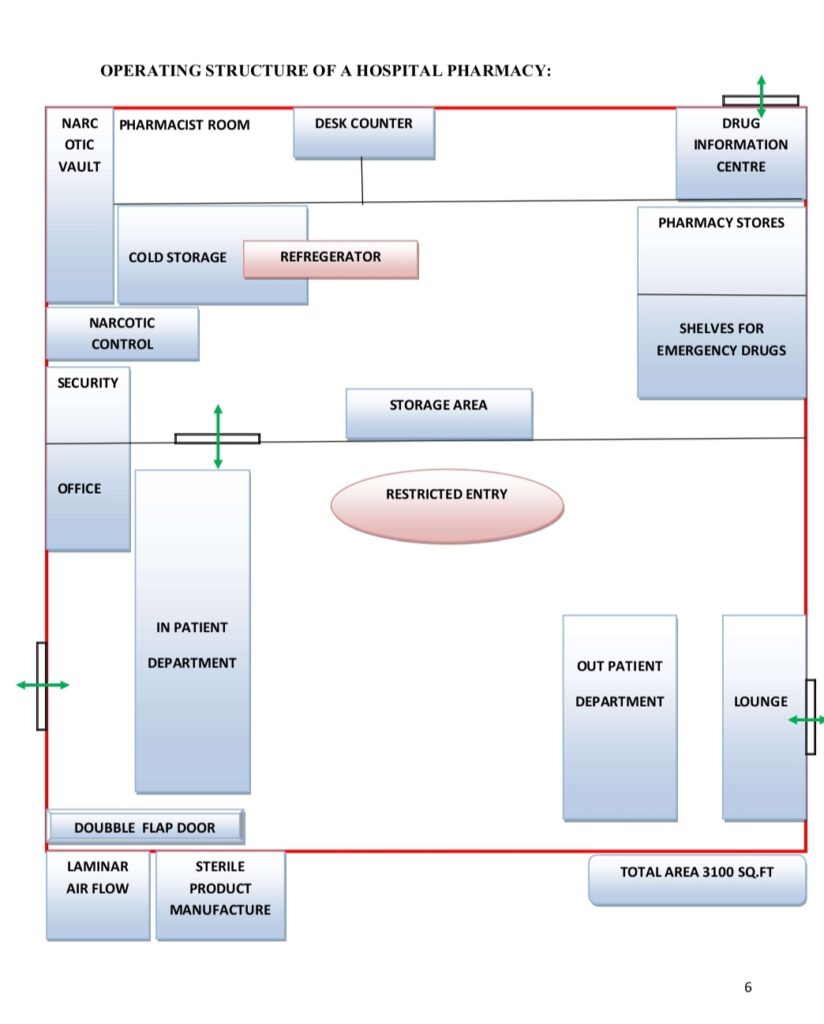
LOCATION & LAYOUT: The location of hospital pharmacy should be in such a way that it is convenient for providing services to all the departments of hospital and personnel who make their daily use. If the hospital is providing outpatient services then pharmacy should be located adjacent to outpatient department. The requirements relating to manufacture of tablets, parentrals, and the preparations must be under aseptic conditions and packing’s are laid in schedule ‘M’ of Drugs & Cosmetic rules.
FLOOR SPACE: A minimum space of 250sq.ft may be allocated for hospital pharmacy. The basic requirement of floor space is 10 sq.ft per bed in 100 bedded hospital and 6 sq.ft per bed in a 200 bedded hospital is required.
INFRACTURE REQUIREMENT: The pharmacist, administrator, architect assume the responsibility of planning, purchasing equipments required by the pharmacy. The equipments are mainly categorized in two types. They are a) Fixed equipments b) Movable equipments Fixed equipments require installation and becomes attached to the building and the movable equipments are placed inside the pharmacy and no need for installation.
FOR OUTPATIENT PHARMACY: a) Fixed equipments: 1) Counter with draw and knee space. 2) Shelves for books. 3) Wall mounted adjustable draws. 4) Shelves with lock & key facility. b) Movable equipments: 1) Adjustable stools and chairs. 2) Refrigerator 3) Computer and printer 4) Cabinets 5) Telephone 6) Waste receptacle.
FOR INPATIENT DISPENSING PHARMACY: 1) Wall mounted cabinets 2) Counter with draw and knee space 3) Pneumatic tube station 4) Autoclave 5) Wash area 6) Hood, laminar air flow 7) Waste receptacle 8) Adjustable shelves 9) Book shelves
10) Chairs for waiting areas etc.
STAFF:
The staff requirements for hospital pharmacy depends on
a) Number of beds in a hospital.
b) Average number of inpatients and out patients
c) Activities of the unit
d) Whether pharmacy also stock, dispense surgical & laboratory supplies etc.
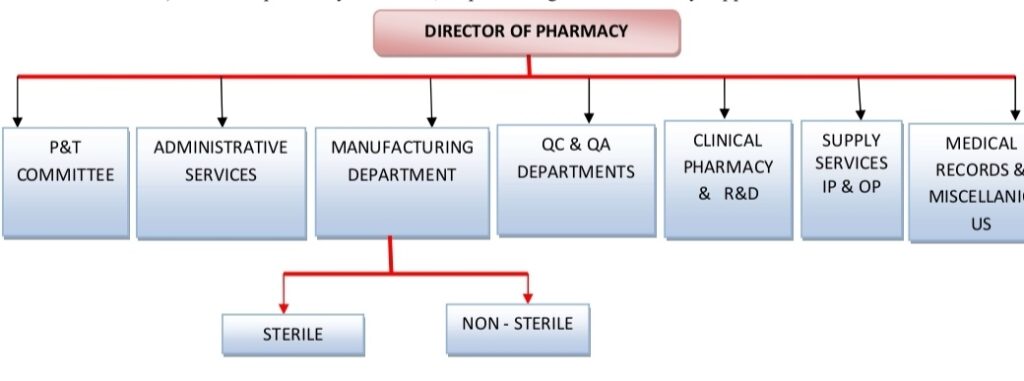
According to the job evaluation guidelines these are
a) One chief pharmacist
b) One registered pharmacist for every 60 inpatients and out patients.
c) One typist cum clerk
d) Adequate number of assistants and attainders.
For a hospital pharmacy involved in manufacture of drugs and formulations These are
a) a deputy chief pharmacist or manufacturing pharmacist
b) one analytical pharmacist
For purchase and inventory control
a) a deputy chief pharmacist with through knowledge of purchasing.
WORK LOAD STATISTICS:
The workload statistics evaluation is mainly based on the flowchart process preparation. Once it
is prepared the pharmacist evaluate the time and motion involved in performance of each job in
each department.
A) OUT PATIENT ACTIVITY CHART:

B) IN PATIENT ACTIVITY CHART:
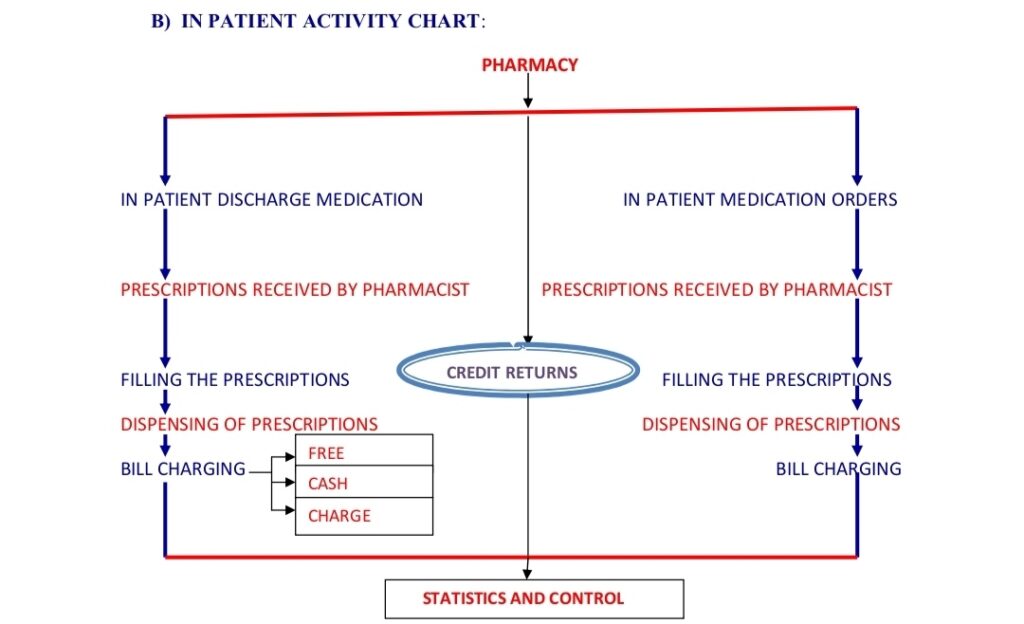
Pharmacist perform the works in manufacturing sections like
a) Weighing of ingredients
b) Mixing of ingredients
c) Taking orders on telephones or by mails.
d) Providing information
e) Maintaining all records
f) Training apprentice
g) Organizing awareness camps
h) R & D activities.
The supportive personnel under the supervision of a registerd pharmacist perform the
functions of
a) Inventory supplies & restocking prescription items.
b) Calculate the prize of prescriptions dispensed.
c) Clean bulk manufacturing and preparing the equipment.
d) Delivery of drugs to wards, nursing stations and to doctors.
e) Pay purchase accounts. Etc.